research report in research methodology

Introduction
In the vast landscape of academic inquiry, research methodologies serve as the compass guiding scholars through the intricate terrain of data collection and analysis. Among the myriad tools in this methodological toolkit, the research report stands as a vital artifact that encapsulates the journey of exploration, discovery, and understanding. It is not merely a document detailing findings; rather, it is a narrative of the research process itself, illuminating the choices made along the way, the challenges faced, and the insights gleaned. In this article, we delve into the nuances of research reports within the context of research methodology. By unpacking their structure, significance, and the critical role they play in the dissemination of knowledge, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of how effective reporting can enhance both the credibility and impact of research. Join us as we explore the foundational elements that make research reports an indispensable part of the scholarly dialogue.
Understanding the Foundations of Research Methodology
Research methodology serves as the backbone of any study, guiding researchers on how to systematically investigate a phenomenon. At its core, it encompasses the principles and methods that inform the research process, ensuring a structured approach to data collection and analysis. Key elements of research methodology include:
- Research Design: The overall strategy that outlines how the research will be conducted.
- Data Collection Methods: Techniques such as surveys, interviews, or experiments used to gather information.
- Data Analysis: Procedures for analyzing collected data to derive meaningful insights.
- Ethical Considerations: Guidelines to ensure integrity and respect for participants.
Understanding these foundations is crucial for the development of a robust research report, as it provides a clear framework that enhances the credibility and reliability of the findings. A well-structured methodology not only details what was done, but also explains why specific methods were chosen. To illustrate the variety of approaches in research, consider the table below:
| Methodology Type | Description | Common Techniques |
|---|---|---|
| Qualitative | Focuses on understanding concepts, thoughts, and experiences. | Interviews, Focus Groups, Content Analysis |
| Quantitative | Involves numerical data to identify patterns and test theories. | Surveys, Experiments, Statistical Analysis |

Navigating Qualitative and Quantitative Approaches
When embarking on a research journey, understanding the distinction between qualitative and quantitative approaches is crucial. Qualitative research delves into the why behind human behavior, exploring participants’ perspectives through methods such as interviews, focus groups, and open-ended surveys. By capturing rich, descriptive data, researchers can uncover nuances in experiences, allowing for a deeper understanding of complex phenomena. This approach fosters an environment where respondents can express themselves fully, often revealing insights that numerical data alone might miss.
In contrast, quantitative research emphasizes the what and how much aspect, utilizing structured tools like surveys with closed-ended questions, experiments, and statistical analysis. This method excels in producing measurable data that can be statistically analyzed, offering a broader view of trends and patterns across larger populations. A combination of both approaches can enhance the depth and breadth of a study, as integrating qualitative insights with quantitative metrics provides a more comprehensive picture. Below is a simplified comparison table to illustrate their main differences:
| Aspect | Qualitative Research | Quantitative Research |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Understanding meanings and experiences | Measuring variables and identifying patterns |
| Data Type | Textual and visual data (words, images) | Numerical data (statistics) |
| Sample Size | Smaller, purposive samples | Larger, random samples |
| Analysis Method | Thematic analysis, coding | Statistical analysis, graphs |
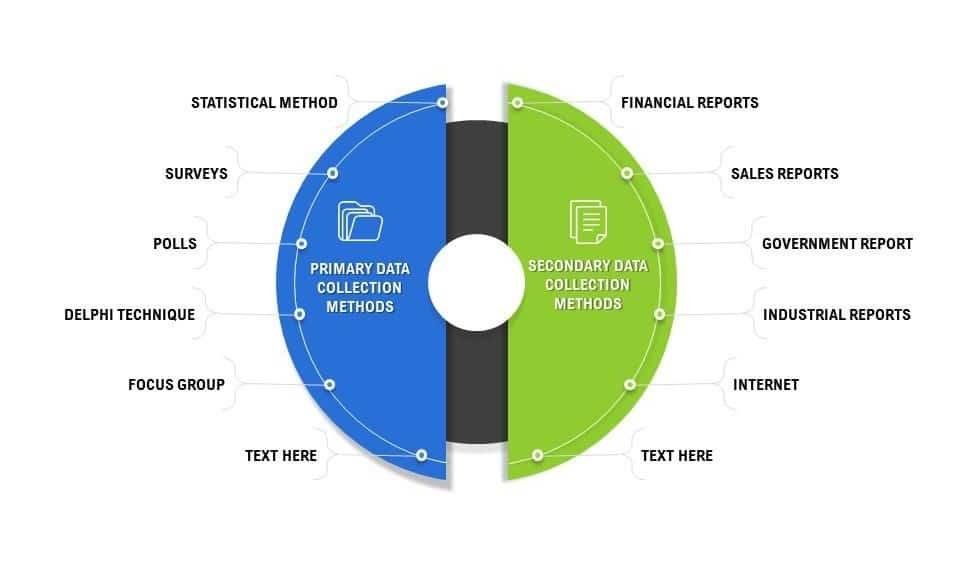
Analyzing Data Collection Techniques for Impactful Insights
In the realm of research methodology, selecting the right data collection techniques is vital for obtaining insights that drive decisions and strategies. Each technique has its own strengths and weaknesses, which can significantly influence the outcome of a study. Commonly employed methods include:
- Surveys: Effective for gathering large volumes of data quickly, especially when targeting specific populations.
- Interviews: Provide in-depth insights through direct engagement, allowing for nuanced understanding of participant perspectives.
- Observations: Facilitate a real-time understanding of behaviors and interactions in natural settings.
- Experiments: Allow for controlled conditions to ascertain causal relationships between variables.
The choice of method will depend on the research objectives, resources available, and the nature of the subject matter. Implementing a mixed-method approach often enhances the rigor and depth of the analysis. By combining qualitative and quantitative techniques, researchers can cross-validate findings and uncover richer narratives. The following table provides a concise comparison of methods based on key attributes:
| Data Collection Method | Strengths | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Surveys | Scalable, quick analysis | Poor response rates, limited context |
| Interviews | Deep insights, flexible | Time-consuming, potential bias |
| Observations | Real-life context, natural behavior | Observer bias, limited generalizability |
| Experiments | Control over variables, causation evidence | Artificial settings, ethical concerns |
Strategies for Effective Reporting and Presentation of Findings
To effectively communicate research findings, it is crucial to create a structured narrative that leads the audience through the data with clarity and precision. Start with a concise executive summary that highlights the key findings and implications of the research. Use visual elements such as graphs, charts, and infographics to illustrate complex data, making it easier for readers to digest. Here are some strategies to enhance the presentation:
- Utilize storytelling techniques: Frame your findings within a story that provides context and meaning.
- Focus on the audience: Tailor your language and complexity level to meet the needs of your target audience.
- Create engaging visuals: Ensure that every visual element serves a purpose and reinforces your central message.
Another aspect to consider is the organization of your report. Clearly labeled sections and effective transitions between topics can greatly enhance readability. Consider using a simple table to summarize key findings or comparisons:
| Finding | Significance |
|---|---|
| Increased engagement by 30% | Demonstrates effective intervention |
| Cost reduction of 20% | Indicates improved resource management |
By implementing these strategies, your research report will not only convey findings effectively but also resonate with your audience, leaving a lasting impact.
To Conclude
delving into the intricacies of research methodology offers a vital framework for investigators navigating the often-turbulent waters of academic inquiry. A well-structured research report not only illuminates the path of discovery but also fosters transparency and rigor in the pursuit of knowledge. By adhering to established methods, researchers can ensure their findings contribute meaningfully to the broader landscape of their respective fields. As we chart the course forward, it is essential to remain adaptable, embracing new methodologies and technologies that continue to shape our understanding. Ultimately, the research report stands as a testament to the collaboration between imagination and systematic study—inviting scholars and practitioners alike to engage in the ongoing dialogue of knowledge creation. In this ever-evolving journey, we are reminded that each report not only represents a culmination of efforts but also serves as a stepping stone toward future inquiries, challenges, and discoveries that await beyond the horizon.




