research lab report

In the realm of scientific inquiry, where curiosity meets methodical investigation, the research lab report stands as a pivotal artifact of the empirical journey. It serves not only as a record of experimentation and discovery but also as a vital communication tool that bridges the gap between researchers and the wider scientific community. Just as an artist meticulously documents their creative process or a historian catalogs significant events, the lab report meticulously chronicles the steps taken in the pursuit of knowledge. In this article, we will explore the essential components and structure of a well-crafted research lab report, illuminating its role in fostering understanding, transparency, and collaboration within science. Whether you are a seasoned researcher or a budding scientist, understanding how to articulate findings effectively is crucial in advancing the collective quest for knowledge. Join us as we delve into the art and science of writing a research lab report, where each word holds the weight of inquiry and innovation.
Understanding the Structure and Components of a Research Lab Report
A well-structured research lab report is essential for clearly communicating scientific findings. Typically, a lab report consists of several key sections, each serving a specific purpose. The introduction establishes the research question and provides background information, while the materials and methods section outlines the experiment’s design and the tools utilized. This transparency is crucial for reproducibility and allows others to verify the results. Following this, the results section presents the data collected, typically incorporating tables and figures for clarity. the discussion interprets the findings, connecting them back to the initial hypothesis and relevant literature.
In addition to the core sections, an effective lab report often includes:
- Abstract: A concise summary of the entire study.
- References: A compilation of sources cited throughout the report.
- Appendices: Supplementary material such as raw data or detailed calculations.
To illustrate how these components fit together, consider the following table summarizing a hypothetical lab report structure:
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Abstract | Brief overview of the research and findings. |
| Introduction | Context and objectives of the research. |
| Materials and Methods | Details about the experimental procedures. |
| Results | Presentation of data in charts and tables. |
| Discussion | Interpretation and implications of the results. |
| References | List of consulted literature and sources. |

Essential Techniques for Accurate Data Collection and Analysis
To ensure the precision of data collection and subsequent analysis, various techniques should be systematically implemented. One fundamental approach involves making use of surveys and questionnaires, where carefully crafted questions yield quantitative data, enabling easy comparison and statistical analysis. Additionally, conducting interviews can provide qualitative insights that explain the numerical data, offering a comprehensive perspective on research questions. Using observation techniques is also vital, as it allows researchers to gather real-time information and phenomena that may not be easily captured through surveys or interviews. Employing experiments further aids in isolating variables and establishing causal relationships, thus enhancing the reliability of collected data.
Accurate data analysis hinges on organizing and processing the data appropriately. Implementation of data cleaning techniques is essential, where outliers and inconsistent entries are addressed to maintain data integrity. Researchers can utilize various analytical tools that assist in statistical evaluation and visualization, such as spreadsheets or specialized software. Data should be categorized to facilitate easier interpretation, allowing trends and patterns to emerge clearly. The following table summarizes effective techniques for both data collection and analysis:
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Surveys | Structured questionnaires that gather quantitative data. |
| Interviews | In-depth discussions providing qualitative insights. |
| Observation | Real-time data collection in natural settings. |
| Experiments | Controlled tests to determine causal relationships. |
| Data Cleaning | Process of correcting or removing inaccurate data. |
| Analytical Tools | Software used for data processing and visualization. |
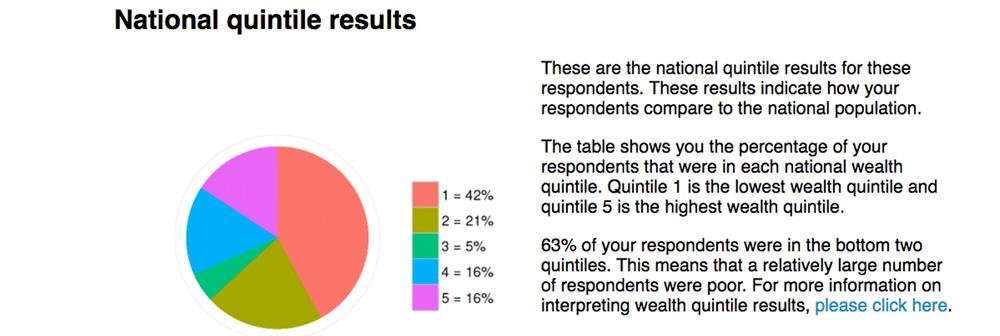
Interpreting Results: Crafting Clear and Compelling Conclusions
Once the data has been collected and analyzed, the next crucial step is to distill those findings into clear and impactful conclusions. Clarity is key; your audience should be able to easily grasp the significance of your results without getting lost in technical jargon. Consider breaking down your findings into manageable insights, focusing on the main themes that emerge from the data. Utilize bullet points to highlight critical outcomes, such as:
- Key trends observed in the experiment.
- Surprising results that challenge previous assumptions.
- Implications for future research or practical applications.
Furthermore, it’s essential to provide context for your conclusions. Explain the ‘why’ behind the results to help your audience understand their relevance. A concise table can effectively summarize comparisons or highlight the main points. For example, the table below illustrates the differences between expected and actual outcomes:
| Expected Outcomes | Actual Outcomes |
|---|---|
| Increase in X by 30% | Increase in X by 25% |
| Reduction in Y | No significant change in Y |
| Improved Z functionality | Enhanced Z functionality noted |
By weaving together both the bare findings and their broader implications, you can create a compelling narrative that not only answers the research questions but also paves the way for future inquiry.

Best Practices for Collaborating and Communicating with Lab Partners
Effective collaboration and communication in a lab environment are essential for successful research outcomes. One of the best ways to foster a cooperative atmosphere is to establish clear roles and responsibilities among team members. This can be achieved through regular meetings where each partner can share their expertise, provide updates, and discuss challenges. Consider implementing a shared digital platform like Google Drive or Microsoft Teams that allows team members to store documents, track progress, and communicate in real-time. This ensures that everyone stays informed and engaged throughout the research process.
In addition to structured communication, fostering a culture of openness can significantly enhance teamwork. Encourage your lab partners to voice their ideas and concerns without fear of judgment. Building this trust will promote a higher level of engagement and creativity. Here are a few tips for maintaining effective communication:
- Schedule Regular Check-Ins: Weekly meetings can help track progress and address any emerging issues.
- Utilize Collaborative Tools: Leverage apps designed for team collaboration to streamline discussions and document sharing.
- Encourage Feedback: Create an environment where constructive criticism is welcomed and appreciated.
Ultimately, the key to successful collaboration lies in understanding and respecting each other’s working styles. Regularly reassessing team dynamics can help you identify areas for improvement. For instance, consider implementing a brief survey to gather feedback on the team’s interaction and workflow. This will not only help in maintaining accountability but also aid in optimizing your collective performance, ensuring a smoother research journey.
| Effective Communication Practices | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Establishing clear roles | Reduces conflict and overlaps |
| Regular meetings | Keeps teams aligned |
| Use of collaborative tools | Enhances organization and access |
| Collecting feedback | Improves team dynamics |
To Conclude
In the intricate world of scientific inquiry, the research lab report stands as a vital beacon of clarity and communication. As we’ve navigated through its essential components—from the structured format to the nuanced analysis of data—we hope to have illuminated the importance of a well-crafted report in the broader tapestry of research. Whether you are a seasoned scientist or a curious student, mastering the art of lab report writing not only enhances the rigor of your findings but also fosters a culture of transparency and collaboration in the scientific community. As you embark on your own research journeys, remember that each report is not just a summary of experiments conducted, but a doorway to new questions, discoveries, and innovations waiting to be explored. Embrace the challenge, refine your skills, and let your reports be a testament to the relentless pursuit of knowledge. After all, each page turned in the realm of science opens the door to uncharted territories and endless possibilities. Happy writing!




